Bogorlab awareness: How COVID-19 Spreads
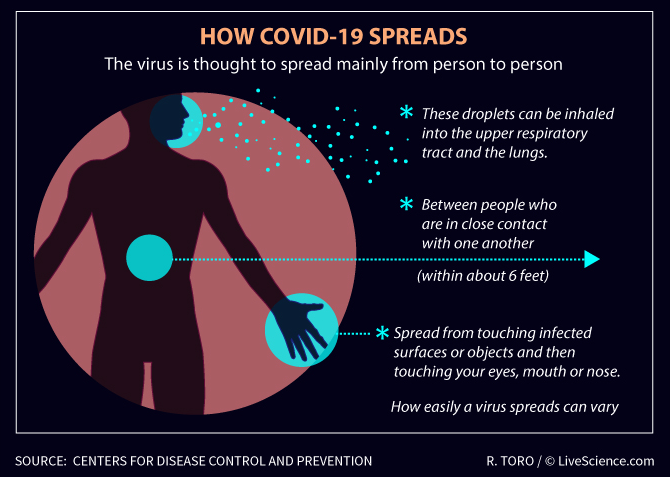

Snapshoot:
It has been suggested that blood type determines the susceptibility level of COVID-19. This level of a vulnerability is based on observations of some COVID-19 patients and their relation to the ability to survive against COVID-19 virus infection
The information contained, group A was more at risk of coronavirus infection, and people with blood type O were considered to be more immune to this virus. This is based on research conducted in China.
Genetic analysis of Covid-19 patients shows that blood type may affect the severity of a person suffering from coronavirus infection. The scientists who compared the genes of thousands of patients in Europe found that those with type A blood tended to experience severe pain, while blood type O was less likely.
During the COVIC-19 pandemic, the use of hand sanitizers was very common. People flocked to use hand sanitizers to avoid spreading the virus to various components through hand contact.
However, there are some hand sanitizers whose use actually causes debate because they contain hazardous chemicals. As reported in the journal of Live Science contain a poisonous substance called methanol, which can be deadly when absorbed through the skin or ingested.
The warning applies to nine hand sanitizer products made by the company, called Eskbiochem, according to a statement from the FDA. The agency said it found methanol in samples taken from several of the company’s products.
To be marketed as a hand sanitizer, a product should contain ethyl alcohol (also called ethanol), isopropyl alcohol (isopropanol) or benzalkonium chloride as the active ingredient, Live Science previously reported.
Full report can be read on
https://www.livescience.com/hand-sanitizer-methanol-fda-warning.html

During a discussion on the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on planning for the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM) Beyond 2020, Monika Gail MacDevette, Chief, Chemicals and Health Branch, UNEP, underscored the need to maintain momentum and raise ambition and partnerships that look at the nexus among the mandates of the chemical conventions.
The post-2020 approach to international chemicals management had been scheduled to be adopted during the fifth session of the International Conference on Chemicals Management (ICCM5) in October 2020. The pandemic caused the postponement of the final preparatory meeting for ICCM5 a few weeks before it was scheduled to take place at the end of March 2020, along with the postponement of ICCM5 itself. Both events are now expected to take place in 2021.
During a webinar organized by the Geneva Environment Network to discuss the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the sound management of chemicals and waste, Nalini Sharma, SAICM Secretariat, noted that the Strategic Approach’s work is connected to the pandemic, particularly through the issue of waste management. She highlighted challenges for SAICM Beyond 2020, including linkages to other agendas, such as biodiversity and climate change. She added that a discussion on linkages between the SAICM Beyond 2020 and the post-2020 global biodiversity framework processes includes identifying activities for better coordination between the two clusters.
Three options for the rescheduled preparatory meeting were identified by Valentina Sierra, Permanent Mission of Uruguay to the UN in Geneva. One option under consideration is early March 2021 in Bucharest, Romania, where it was originally scheduled to take place in March 2020. The other two options are early March 2021, in a back-to-back schedule with the fifth meeting of the UN Environment Assembly (UNEA 5), in Nairobi, Kenya, or early July 2021, in a back-to-back schedule with ICCM5 itself, in Bonn, Germany. ICCM5 has been rescheduled to take place from 5-9 July 2021, in Bonn, Germany.
Sierra reported that small virtual working groups, open online briefings, and submissions of written comments could also contribute to the finalization of outcomes for SAICM Beyond 2020, for adoption at ICCM5. She also called attention to the work of the High-Level Ambition Alliance for chemicals and waste, which seeks to raise awareness and ensure commitment for action on chemicals and waste management.
Representatives from Geneva-based UN agencies discussed the linkages between chemicals management and the issues that their organizations focus on. Manal Azzi, Senior Specialist on Occupational Safety and Health, International Labour Organization (ILO), stressed the importance of the ILO in the chemicals’ field, notably because of workers’ exposure to chemicals along the entire supply chain. Carolyn Vickers, Head, Chemical Safety and Health Unit, World Health Organization (WHO), emphasized the WHO Chemicals Roadmap, and establishment of a global chemicals and health network, where national ministries network to facilitate the implementation of the roadmap. Vickers highlighted that mentioned at least 1.6 million deaths could be prevented by the sound management of chemicals and waste.
Discussing the role of civil society in the Beyond 2020 process, Giulia Carlini, Center for International Environmental Law, said the July 2021 ICCM5 and BRS COPs in Bonn, Germany, would disadvantage non-European participants. She said an online process, including virtual working group sessions and technical briefings, would ensure meaningful and effective participation going forward.
The webinar was part of the GENeva Environment Dialogues’ special bi-weekly COVID-19 series, which focus on the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the global environmental agenda.
The verification process is a test of the performance of standard methods. This verification is carried out on a standard method before it is applied in the laboratory. Verification of a method intends to prove that the laboratory concerned is capable of testing with that method with valid results. Besides verification also aims to prove that the laboratory has performance data. This is because different laboratories have different conditions and personnel competencies and equipment capabilities. Thus, the performance of one laboratory with other laboratories is not the same.
Discoursing laboratories, of course we will never be separated from the main 3M, namely man as human resources, machines in the form of laboratory equipment and materials in the form of laboratory materials. Apart from the 3M, there is still one M which is very important for a laboratory, namely the testing method. Test methods that are proven to be applicable in a laboratory will produce valid test information for decision making and even a diagnosis.
Some parameter for validation methods include the following:
Accuracy
is a measure that shows the degree of closeness of the chemical comparison results added to the mixture of pharmaceutical preparations (placebo) carriers and then the mixture is analyzed and the results are compared with the levels of the analytes added (actual levels).
Precision
Is a measure that shows the degree of concordance between individual test results, measured by the distribution of individual results from the average if the procedure is applied repeatedly to samples taken from a homogeneous mixture.
Selectivity (Specificity)
It is his ability to only measure certain substances carefully and thoroughly in the presence of other components that may be present in the sample matrix.
Linearity
is the ability of the analytical method to provide a response that is directly or with the help of an ideal mathematical transformation achieved if the value of b = 0 and r = +1 or –1 depending on the direction of the line.
Detection Limits and Quantitation Limits
Ruggedness method
Is the degree of confusion of the test results obtained from the analysis of the same sample under various normal test conditions, such as laboratories, analyzes, instruments, reagents, temperature, different days, etc.
Strength (Robustness)
(Source: Harmita, 2004)
For some laboratories that have used standard methods, it is usually sufficient to test with a minimum of three parameters. Validation / verification of this testing method applies to all methods both qualitative and quantitative.
Climate change that is happening right now is very much influenced by human behavior and its surroundings. The increasing amount of land use for human settlements has caused changes in the landscape and the environment.
Valid environmental data when they are accessible and available will be obtained from competent environmental laboratories. For this reason, the Research and Development Center for Quality and Environmental Laboratory anywhere will have function to provide mentoring guidance, and technical guidance in the framework of building credible environmental laboratory and acceleration. The environmental laboratory also assists in the management of the provision of the environmental field, which is implemented through the provision of laboratory facilities and infrastructure in any areas of operation. [both provincial and district / city level].
The role of the environmental laboratory at this time is needed to become one of the measuring and validation tools for sustainable environmental management. Why sustainable? Of course, we hope that environmental management will have a positive impact and minimize the negative impacts arising from such development.
Many management activities in an area require scientific evidence such as water quality standards and responsible waste management. The role of the environmental testing laboratory bridges these management activities by proving and demonstrating evidence.
Bogorlab is a testing laboratory located in Bogor Indonesia where an Agricultural Institution has been the center of knowledge development in this City. Our laboratory testing services are available for extensive quality control and assurance programs.
At present adequate services of the environmental laboratories are urgently needed. The laboratory needs to support the verification of a certain site or certain area that is managed in an environmentally friendly manner.
Given the task of the existence of the Environmental Laboratory Technical Unit is to assist Agencies related to environmental management in laboratory testing and analysis and its development. The laboratory functions in the presentation of data and information in the environmental field and conduct laboratory testing and analysis for all environmental components. In addition, it is also important to carry out Technical Development and environmental laboratory analysis methods in accordance with laboratory quality systems and applicable standards.